Search This Blog
Most Popular
Categories
- Building Construction (87)
- Building Materials (88)
- Columns (2)
- Concrete Beam (3)
- Concrete Construction Techniques (6)
- Concrete Mix Design (15)
- Concrete Repair (14)
- Concrete Slab (11)
- Construction Equipment (17)
- Construction News (7)
- Design of Structures (20)
- Engineering Drawing (1)
- Estimation (3)
- Geotechnical engineering (26)
- Highway Engineering (11)
- Innovations (34)
- Material Testing (11)
- Matrix Analysis of Structures (2)
- Mechanical Engineering (3)
- Strength of Materials (2)
- Structural Analysis (13)
- Structural Design (24)
- Structures (17)
- Transportation Engineering (9)
Boring Methods for Soil Exploration
Team Prodyogi
November 02, 2023
Boring in soil investigation is the process of collecting soil samples from the construction site by drilling holes using specialized equipment. As we know, soil sampling is the first major step conducted in soil exploration or investigation of a construction site. The process is followed by in-situ & laboratory tests on the collected samples.
Boring methods are of several types like auger boring, rotary drilling, wash boring, percussion drilling, auger drilling, and test pits. These tests can be conducted to collect both undisturbed and disturbed soil samples for required test specifications.
This article is a comprehensive guide to different boring methods and their applications in construction site soil exploration.
1. Auger Method
The Auger method is the simplest of all the boring methods. This method drill augers into the soil to collect the sample. The auger drill used can be hand-operated or power-driven based on the type of soil.
During the process, the soil augur is drilled into the soil. The boreholes formed are dry and unsupported. When the augur gets filled with the soil, it is taken out and the soil sample is collected.
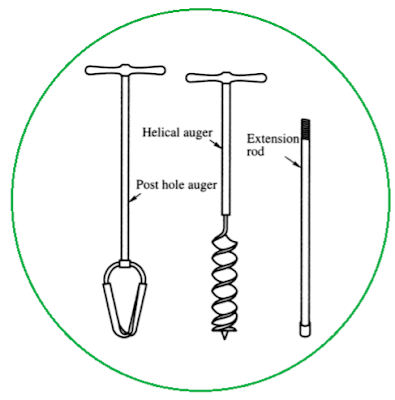
1.1. Hand Operated Augers
The hand-operated augur drilling method can collect samples from a depth of up to 10m. It is suitable for all soil types above the water table and clayey soil below the water table. The hand-operated augur consists of a string of drill rods that are used to advance the drilling movement downwards.
 |
| Fig.2. Hand Augers Types |
The hole drilled takes a diameter between 10 to 20 cm. Hand augering is not suitable for stiff, very hard, granular soils below the water table. It is not practicable in dense sand nor in sand mixed with gravel even if it lies above the water table.
1.2. Power Driven Augers
Power-driven continuous flight augers are the most popular method of soil exploration for boring holes. The method is suitable to drill holes up to 60 m. This method is suitable for all soil types including the layers below the water table, but not suitable for soil mixed with gravel, cobbles, etc.
 |
| Fig.3. Power Driven Auger |
As shown in Fig. 3, the central stem of the auger flight may be hollow or solid. The drilling rig is mounted to a tractor or truck during the process.
The soil sample collected by the auger method is disturbed. The method is suitable for soft to stiff cohesive soil and can also be used to determine the groundwater table. It is not suitable for very hard or cemented soil, and very soft soils.
2. Wash Boring
Wash boring is used for soil exploration below the ground water table which is very difficult to perform by means of pits or auger boring. High-pressure water and washing are performed while drilling the hole. Suitable for sand, silt, or clay and not for soil mixed with gravel or boulders. It is used to collect undisturbed and disturbed soil samples.
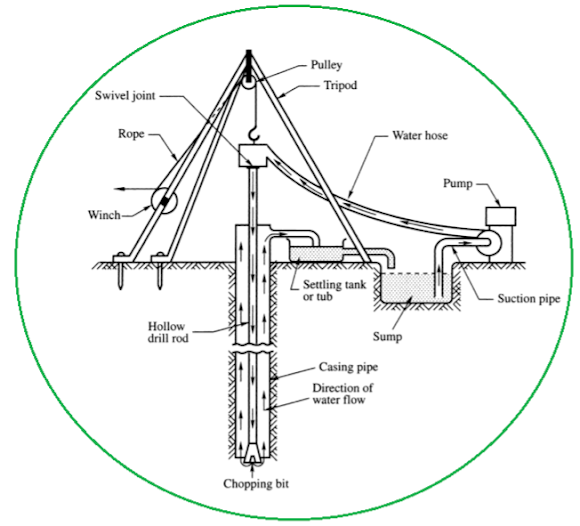 |
| Fig.4. Wash Boring Method |
As shown in Fig.4, wash boring starts with the advancing hole to a short depth by means of an auger. Along with this, a casing pipe is pushed to prevent the sides from caving. The hole is continued drilling by means of a chopping bit fixed at the end of a string of hollow drill rods. The whole process is driven by mechanical or manpower. The bit is screwed to a string of hollow drill rods that is supported on a tripod by a rope or steel cable passing over a pulley as shown in the figure.
A stream of water under pressure is forced through the rod and bit into the hole, which loosens the soil as the water flows up around the pipe. The loosened soil is discharged into a tub. Once the suspended soil settles, the water is reused for circulation.
The normal process gives disturbed washed samples for analysis. When undisturbed samples are required, the boring is stopped and the chopping bit is replaced by a sampler. This sampler is pushed into the soil at the bottom of the hole and the sample is withdrawn.
4. Rotary Drilling
Rotary drilling method of boring is used to drill highly resistant strata like finding rock strata, and access the quality of the rocks from cracks, fissures, and joints. They can be used to take disturbed and undisturbed soil samples. The maximum depth it can work is 70 m and higher based on the capacity of the equipment.
As shown in fig.5, the string of drill rods has a cutter bit or core barrel with a coring bit at its end. This drill rod is rotated and penetrated into the soil by a power rig. The drilling involves chipping the material followed by washing out the loose materials by means of a stream of water as in wash boring. Cutter bit is used for soil boring while core barrel is used in rocky strata to get rocky samples.
During the penetration, a drilling fluid is introduced into the bottom of the hole through the passages in the hollow drill rods. This fluid serves the function of both cooling the drilling bit and removing the cuttings from the bottom of the hole.
Rotary drilling is mostly performed without casing. During the process, the drilling fluid acts as a casing during the sample collection.
To collect soil samples, the drilling bit is replaced with a sampler to obtain the sample. But for rock strata, we use a coring bit at the time of collecting rock samples. In the meantime, the rotary drilling equipment arrangement can also be used for wash boring and auger boring.
5. Percussion Drilling
Percussion drilling is a method of boring commonly used for river deposits with hard boulders of quarzitic types. In this method, heavy drilling bits are raised and dropped in such a manner that it powders the underlying materials which forms a slurry with water. This is later removed as the boring advances.
 |
| Fig.6. Percussion Drilling |
Percussion drilling can be used for sample collection at a depth greater than 70 m. The method is commonly used for disturbed samples as the quality of undisturbed samples is affected due to their blows.
After understanding the types of boring methods used for soil sampling, we move on to the various sampling methods. Here we will study various samplers used to collect undisturbed samples, as they require a unique setting. Followed by which we perform different tests on samples to determine the soil parameters.
Continue Reading On: Soil Sampling Methods in Soil Exploration
Most Visited
Soil Sampling Methods| Undisturbed and Disturbed Samples
November 08, 2023
Boring Methods for Soil Exploration
November 02, 2023
Steel Column Connected to Concrete Masonry Wall
October 11, 2017
What is Development Length (Ld) in Construction?
August 14, 2025
How to Choose Good Quality Aggregates for Construction?
August 10, 2021
Structure of Timber |Macrostructure and Microstructure
March 22, 2024
What are Infiltration Wells?
April 15, 2024
Search This Blog
MUST READ
What is PERT? Objectives, Pros & Cons
September 10, 2017
Terzaghi's Equation: Soil Bearing Capacity for Foundations
March 02, 2022
Contact Form
Footer Menu Widget
Created By SoraTemplates | Distributed By Gooyaabi Templates



0 Comments
Commenting Spam Links Are Against Policies