Search This Blog
Most Popular
What is Rendering in Construction? Types & Benefits
September 18, 2023
Soak Pit - Function, Types & Design
September 15, 2023
Categories
- Building Construction (86)
- Building Materials (83)
- Columns (2)
- Concrete Beam (3)
- Concrete Construction Techniques (4)
- Concrete Mix Design (13)
- Concrete Repair (14)
- Concrete Slab (10)
- Construction Equipment (16)
- Construction News (7)
- Design of Structures (15)
- Engineering Drawing (1)
- Estimation (3)
- Geotechnical engineering (26)
- Highway Engineering (11)
- Innovations (32)
- Material Testing (10)
- Matrix Analysis of Structures (2)
- Mechanical Engineering (3)
- Strength of Materials (2)
- Structural Analysis (13)
- Structural Design (22)
- Structures (17)
- Transportation Engineering (9)
Glass Fiber Reinforced Gypsum (GFRG) Construction Material
Neenu
January 22, 2022
GFRG is Glass Fiber Reinforced Gypsum is a gypsum construction material that was initially developed from England to the United States and Canada in 1977, and came into use since 1990. The product is form of gypsum plaster reinforced with glass fibers to produce a thin, lightweight, and a stronger material. GFRG is also called as fiberglass reinforced gypsum (FRG) and Glass Reinforced Gypsum (GRG).
 |
| GFRG Panel Building Construction Image Courtesy: Click.in |
GFRG is mainly used as an interior alternative for Glass Fiber Reinforced Concrete (GFRC). GFRC is mainly used for exterior applications.
We will discuss the composition, properties and various applications of GFRG in constructing a building.
Fabrication of GFRG
The composition of GFRG are:
- High-density alpha-based gypsum
- Glass fiber reinforcement
The gypsum plaster should be neutral or low alkaline to ensure its compatibility with "E" glass fibers. The additives commonly used with gypsum manufacturer's recommendations.
GFRG are manufactured as panels of thickness of 124 mm under careful controlled conditions to a length of 12 m and height of 3m. They are manufactured with cavities, that are unfilled, partially filled or fully filled with reinforced concrete as per the structural requirement and applications.
A good quality GFRG panels are selected based on:
- Zero-VOC alpha-gypsum mined in the USA
- Glass mat incorporated for strength
- ASTM testing including the all-important ASTM E84 (0/0 smoke/flame)
- 2.5 lbs./ft² high strength composition
- LEED supported
Applications of GFRG
The general category of applications of GFRG panels in building construction are:
- Load bearing walls
- Partition walls
- Compound and security walls
- Horizontal floor slabs or roof slabs
1. Load Bearing Walls
GFRG panels with cavities that are filled with reinforced concrete can be used as load bearing walls for multistoried housing. For single/two-storey construction, the cavities can remain unfilled or filled using structural core filling materials like insulation, quarry, dust, sand, polyurethane or lightweight concrete.
2. Partition Walls
Partition walls are used as multi storied frame buildings, that can be filled suitably. These walls can also be used for cladding installation for industrial or sport facilities etc.
3. Compound Wall Construction
Low and cheap compound walls or security walls can be constructed.
4. Horizontal floor slabs or roof slabs
Horizontal floor slabs or roof slabs with reinforced concrete micro beams and screed (T-beam action). This system can also be used in inclined configuration, like staircase waist slab and pitched roofing.
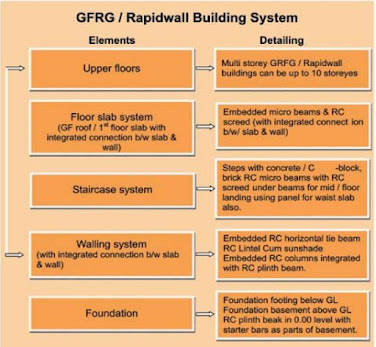
GFRG Building System
Mechanical Properties of Glass Fiber Reinforced Gypsum (GFRG)
Advantages of GFRG in Building Construction
The main advantages of GFRG in building construction are:
- Flame resistant
- Ease of installation
- Provide good finish
- Thermal resistant
How to get Quality GFRG?
A. Manufacturer’s Qualifications:
- Obtain GFRG from a manufacturer who will, upon request, send a qualified technical representative to the project site for the purpose of advising the installer of procedures and precautions for materials used.
- Obtain GFRG from a manufacturer who will certify the materials have been tested and proven satisfactory for the intended use.
- Obtain GFRG from a manufacturer with five years verifiable and successful experience producing material for projects of similar size and scope. GFRG must be manufactured in the United States.
B. Installer’s Qualifications:
- Firm must provide evidence of three years verifiable evidence installing the specified work.
- Installer must be acceptable to the manufacturer.
Tests on Characteristic Properties of GFRG Panels
- Tensile Strength - Tested as per ASTM Test Method D638-14
- Compressive Strength - ASTM Test Method C170 21.4 MPa
- Flammability - ASTM Test Method E84
- Barcol Hardness - ASTM Test Method D2583-13a
- Coefficient of Linear Thermal Expansion - ASTM Test Method D696
- Water Absorption - BS EN 520 : 2004 + A1:2009
Read More On: Building Construction Materials
Most Visited
Sieve Analysis of Aggregates - ASTM Standard
August 11, 2021
How to Choose Good Quality Aggregates for Construction?
August 10, 2021
What are Infiltration Wells?
April 15, 2024
How to Calculate Cement Required for Floor Tiling?
July 02, 2020
Wall Ties or Brick Ties in Construction
June 13, 2022
What is a Cap Beam?
May 15, 2025
Top 7 Waterproofing Materials for Concrete Roofs
December 13, 2024
What is Target Mean Strength? R.C.C Design
July 17, 2021
Construction ERP System – A Comprehensive Guide
December 12, 2024
Search This Blog
MUST READ
What is PERT? Objectives, Pros & Cons
September 10, 2017
Terzaghi's Equation: Soil Bearing Capacity for Foundations
March 02, 2022
Contact Form
Footer Menu Widget
Created By SoraTemplates | Distributed By Gooyaabi Templates


0 Comments
Commenting Spam Links Are Against Policies