Search This Blog
Most Popular
Categories
- Building Construction (87)
- Building Materials (85)
- Columns (2)
- Concrete Beam (3)
- Concrete Construction Techniques (6)
- Concrete Mix Design (15)
- Concrete Repair (14)
- Concrete Slab (11)
- Construction Equipment (17)
- Construction News (7)
- Design of Structures (19)
- Engineering Drawing (1)
- Estimation (3)
- Geotechnical engineering (26)
- Highway Engineering (11)
- Innovations (34)
- Material Testing (11)
- Matrix Analysis of Structures (2)
- Mechanical Engineering (3)
- Strength of Materials (2)
- Structural Analysis (13)
- Structural Design (24)
- Structures (17)
- Transportation Engineering (9)
Testing and Quality Control of Mortar
Team Prodyogi
September 15, 2020
When it comes to ensuring the strength and quality of mortar used in construction projects, rigorous testing is essential. Testing methods provide valuable insights into the performance and durability of mortar, helping builders and engineers make informed decisions.
Here's an enlisted overview of measures and processes commonly implemented to ensure quality control of mortar:
By implementing these measures and processes, construction professionals can ensure that the mortar used in their projects meets the required standards, resulting in reliable and high-quality construction outcomes.
In this blog post, we will delve into the world of mortar testing, exploring the key tests used to assess its properties and characteristics. From measuring tensile and crushing strength to evaluating adhesiveness, we'll uncover the significance of these tests and how they contribute to constructing safe and reliable structures.
What are the General Tests on Mortar?
The general tests on mortar are:
Quality control of mortar refers to the systematic measures and processes implemented to ensure that the mortar used in construction projects meets specific standards and requirements. It involves monitoring and evaluating various aspects of mortar, such as its composition, consistency, workability, strength, and other performance characteristics.
- Adhesive test on Mortar
- Crushing Strength test on Mortar
- Tensile Strength Test on Mortar
1. Adhesive Test on Mortar
To test the adhesive capacity of the mortar with the building units, two bricks are placed one over the other at right angles to each other. The mortar is placed to join them. This will form a horizontal joint. The upper brick is suspended from an overhead support and the weights are attached to the lower brick.
The weights are increased till the brick separates. Then,
Ultimate Adhesive Strength = Maximum Load/Area of Contact
2. Crushing Strength Test on Mortar
A sample of brickwork with specified dimensions is taken and loaded under compression testing machines. The test is applied till the failure occurs due to crushing.The ultimate crushing strength is calculated as;
Ultimate crushing strength of mortar = Maximum load/ Cross-sectional Area
3. Tensile Strength Test on Mortar
Briquette molds are used to test the tensile strength of mortar. After curing the briquettes are tested in a tension testing machine.
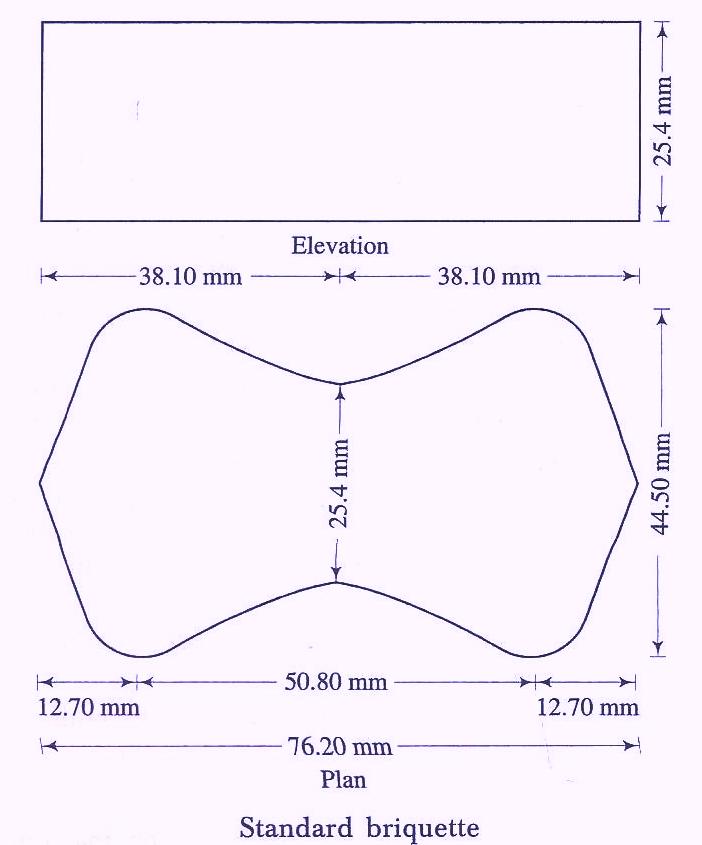
Ultimate tensile stress = Load at Failure/ Cross-Sectional Area [ At the Central Portion]
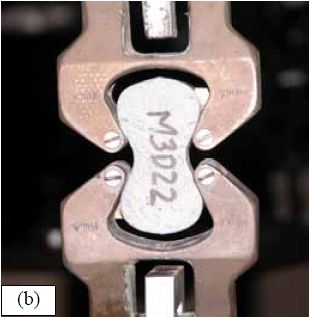
This test method, described in AASHTO T132, normally involves the direct tension testing of a small briquette cast from cement mortar
Quality Control of Mortar in Construction
1. Raw Material Selection
- Ensuring the use of high-quality cement, sand, and additives.
- Verifying the conformity of raw materials with relevant standards and specifications.
- Conducting periodic inspections of incoming materials for consistency and quality.
2. Proportions and Mixing
- Following standardized mixing ratios and proportions for different mortar types.
- Using accurate measuring techniques to ensure precise ingredient quantities.
- Employing efficient mixing methods (e.g., mechanical mixers) to achieve uniformity.
3. Consistency and Workability
- Regularly assessing the consistency and workability of mortar batches.
- Conducting slump tests to determine the flow and ease of application.
- Adjusting water content or additives as necessary to achieve desired consistency.
4. Strength Testing
- Performing compressive strength tests on mortar samples.
- Conducting these tests at predetermined intervals to monitor strength development.
- Comparing test results with specified strength requirements for the intended application.
5. Adhesion and Bond Strength
- Evaluating the bond strength between mortar and various substrates.
- Conducting pull-off tests to measure the adhesive strength.
- Ensuring proper surface preparation and adequate curing conditions for accurate results.
6. Setting Time
- Monitoring and recording the initial and final setting times of the mortar.
- Adhering to specific setting time requirements based on project specifications.
- Adjusting mix proportions or using additives to control setting time, if necessary.
7. Quality Assurance Inspections
- Conducting regular inspections of mortar applications on-site.
- Checking for proper mortar coverage, uniformity, and absence of defects.
- Identifying and rectifying any issues or deviations promptly.
8. Documentation and Record Keeping
- Maintaining detailed records of raw material sources, batch proportions, and test results.
- Documenting quality control procedures followed during production and application.
- Creating a traceable quality control history for future reference and quality assurance.
By implementing these measures and processes, construction professionals can ensure that the mortar used in their projects meets the required standards, resulting in reliable and high-quality construction outcomes.
Most Visited
Soil Sampling Methods| Undisturbed and Disturbed Samples
November 08, 2023
Boring Methods for Soil Exploration
November 02, 2023
What are Infiltration Wells?
April 15, 2024
Steel Column Connected to Concrete Masonry Wall
October 11, 2017
How to Choose Good Quality Aggregates for Construction?
August 10, 2021
Terzaghi's Equation: Soil Bearing Capacity for Foundations
March 02, 2022
Structure of Timber |Macrostructure and Microstructure
March 22, 2024
Search This Blog
MUST READ
What is PERT? Objectives, Pros & Cons
September 10, 2017
Terzaghi's Equation: Soil Bearing Capacity for Foundations
March 02, 2022
Contact Form
Footer Menu Widget
Created By SoraTemplates | Distributed By Gooyaabi Templates



0 Comments
Commenting Spam Links Are Against Policies